Logistics management works with demand forecasting and inventory management to ensure that a company has enough items in its warehouse to fill orders at various points in time. This includes keeping track of inventory levels, estimating demand, and modifying manufacturing and purchasing plans accordingly.
A fashion clothes company is one example of this. They employ logistics management to manage inventory levels and estimate product demand. They employ inventory management systems to track the stock levels of various items and demand forecasting software to estimate future demand. They also utilize supply chain management approaches to ensure that the goods are delivered to the right place at the right time.
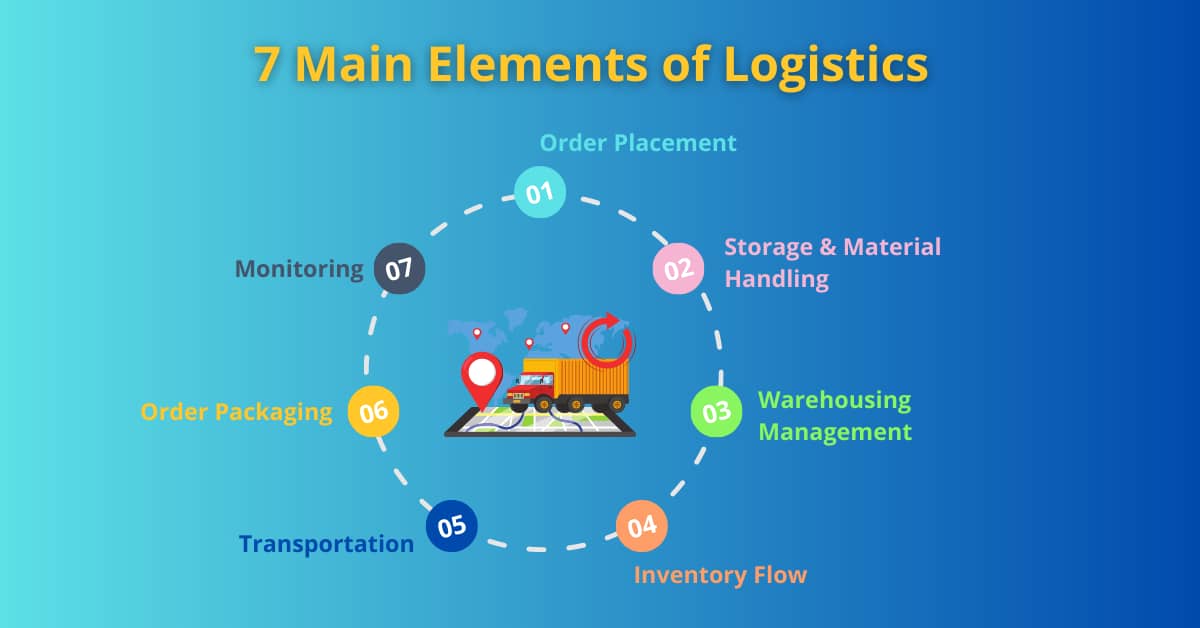
There are 7 main elements in Logistics:
- Order Placement
- Storage and Material Handling
- Warehousing Management
- Inventory Flow
- Transportation
- Order Packaging
- Monitoring
1. Order Placement:
Order processing must be completed by a logistics firm. The initial step in logistics is order processing. This may be the responsibility of the company’s commercial department. The commercial department ensures that payment and delivery terms are met prior to processing orders inside the organization.
For order processing, a logistics company takes the following steps:
- Examining the order for departures from the agreed-upon or negotiated terms.
- Prices, delivery times, payment options, and delivery schedules are all readily available.
- Inquire about the stock availability of supplies.
- In the event of a shortage, planning, and production are essential.
- Recognize the sequence and note any deviations.
2. Storage and Material Handling:
The act or process of moving things around a warehouse is known as material handling. This includes inventory management so that orders can be filled swiftly and properly. Although it may appear to be a simple task, it is critical and must be performed on a regular basis.
Moving one item from a small shop with 100 products is simple. If the shopkeeper isn’t sure where the products are kept, he’ll have to look for them every time a customer places an order. He has 100 products in his inventory and must sift through them before moving any more. Multiply the preceding scenario by 100. Large company warehouses can be up to half a km long.
Consider how many inventory items are kept in the warehouse. If the warehouse manager does not know how to deliver the cargo to the dispatch centre, he will be in big danger. His productivity and efficiency will suffer significantly. The function of material handling is critical.
3. Warehousing Management:
Take, for example, LG and Samsung. These are long-lasting consumer brands having a global presence. Even though their items are manufactured in one location, they are distributed globally. Warehousing is a major Logistics activity with a large influence.
To transport items promptly, the warehouse must be close to the distributor or retailer. A branded good may take longer to arrive than a similar-named product. As a result, it makes sense for a branded company to have a handier warehouse to deliver products more rapidly. The first step for a brand entering a new market is to rent a warehouse. This will allow it to be closer to its consumers and the surrounding community.
This is a rather regular occurrence. This is standard procedure. These warehouses can alleviate delivery pressure and become interdependent, ensuring that customers receive their goods even when demand is high, or output is low.
4. Inventory Flow:
Inventory management is one of the most critical functions of a logistics company. It is about maintaining enough inventory on hand to meet client demand while keeping the expense of carrying products too low. It boils down to balancing the desire to provide exceptional customer service with the need to avoid losing market share.
Although a company may have 100 units on hand, only 10 are required to meet demand. It squandered money by purchasing 90 items. Another company ordered 500 machines, but only 200 were produced since they expected less demand. They have lost sales as well as opportunities.
Logistics companies use software to efficiently manage inventory. This program allows typical tasks, such as assessing how many things are left in a warehouse, to be solved without the need for a physical examination. Each inventory process must be recorded to optimize time and precision. This will allow you to make more space, save money, and minimize trash.
5. Transportation:
Transportation is the most vital activity for a logistics organization. It is also one of the most resource-intensive and revenue-generating divisions of the logistics industry. Fuel is one of the reasons, transportation is so expensive. Fuel, whether petrol, diesel, or natural gas, is an extremely expensive resource that is largely utilized for transportation. According to the order shipment, the logistics provider must obtain LCL and FCL.
Companies invest hundreds of dollars each year to keep transportation costs under control. It is a significant source of business variation. The physical distribution of products from the manufacturer to the distributor or dealer, and ultimately to the final customers, is referred to as transportation.
6. Order Packaging:
There are two types of packaging seen in supermarkets and hypermarkets. The first is the one that customers see on the shelf. It appeals to them and entices them to purchase the package. The second kind is transportation packaging. This permits the product to be safely transported from one location to another without being broken or split.
The logistics business oversees packing the merchandise as cheaply as possible. If necessary, safeguards are not followed, and end customers’ goods may be damaged. This might result in significant losses for both logistics businesses and end users. Packaging might cost as low as 1-2 percent of the real value of the product.
7. Monitoring:
Inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and other data must be tracked by logistics businesses. Each location, for example, requires ongoing information about its status, future commitments, and replenishment capacities.
In a similar manner to the previous stage, the logistics company should investigate the expenses of various means of transportation as well as their suitability for additional products and services. It’s critical to maintain track of logistics information including space utilization and work schedules, order requests, and delivery. By monitoring and assessing total delivery efficacy, logistic businesses may help boost efficiency.
To summarize, these are some of the essential components of logistics management that assist businesses in lowering operational costs and ensuring the execution of key supply chain operations. As a result, a good logistics strategy incorporates cutting-edge features and functionalities to enhance the client experience. Transportation advancements have a significant impact on the components of logistics.