When a company grows and serves more clients in new markets with more services and goods, a decision must be made about whether to outsource its shipping and fulfillment functions.
Many of these companies rely on a third-party logistics (3PL) supplier to help them satisfy consumer demand.
However, not all 3PLs provide the same skills and services.
HOW DO THIRD-PARTY LOGISTICS WORK?
An example of a 3PL service provider setup in action is given below: A publisher of books employs, writers, editors, and graphic designers to create publications, but it might not wish to take on the responsibility of handling customer orders or shipping book shipments. The book publisher, on the other hand, employs a trucking company to transport its goods and a fulfillment Centre to handle its online orders. Both the fulfillment center and the carrier serve as 3PL suppliers. Book orders can also be filled and shipped by a single 3PL provider.
By working with a 3PL supplier, the book publisher can use supply and distribution services only as needed, more effectively managing costs while concentrating on what it does best: publishing books.
What Is Third-Party Logistics?

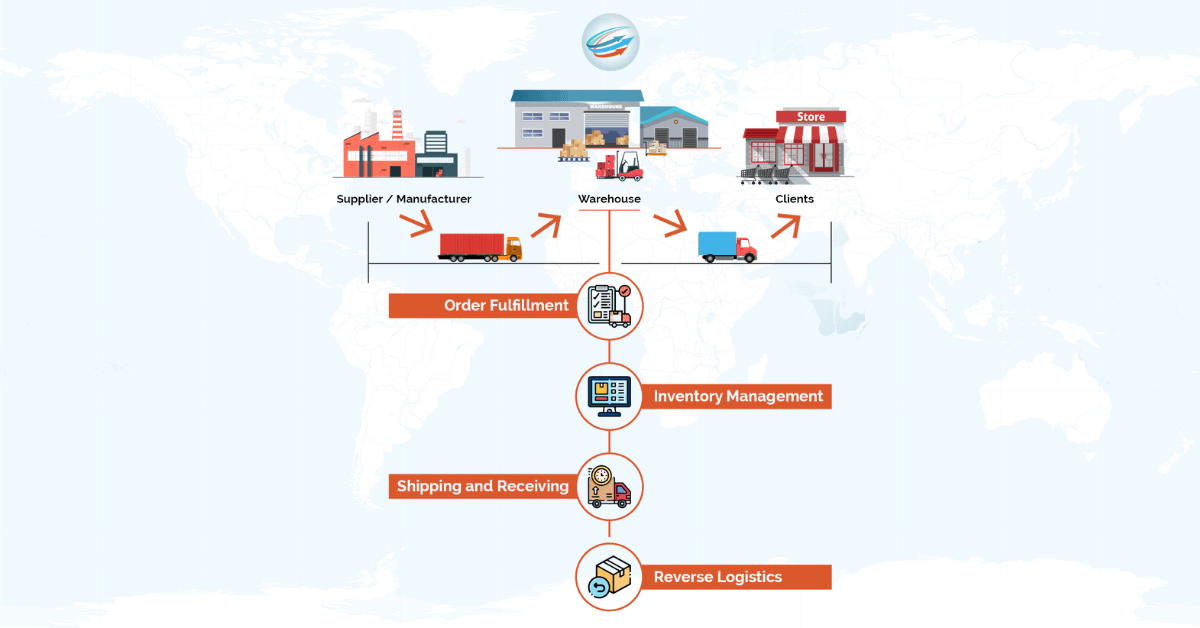
The management of all aspects of transferring goods from producers and distributors to the final consumer is handled by third-party logistics organizations, which provide logistics services and assist some or all components of a company’s shipping operations. In supply chain management and outsourced logistics, a 3PL is frequently used to contract out a company’s shipping and fulfillment functions, which can include:
- Transportation
- Warehousing management
- Materials procurement
- Inventory management
- Customs brokerage or clearance
- Freight auditing
- Payments
- Shipment monitoring
To provide a seamless delivery workflow, a 3PL is typically integrated with a company’s transportation and warehouse management operations.
As well as the domestic and international shipping, trade compliance, and customs brokerage, some 3PLs also develop and provide multimodal logistics solutions for manufacturers, retailers, and e-commerce businesses.
Main Function of 3PL Service Provider
1. Receiving and Shipping
Receiving and shipping the management of the shipping process from beginning to end is the primary focus of 3PL companies. These businesses frequently offer technology, usually in the form of integrated freight management services or a transportation management system (TMS). These technologies were created to increase productivity and automate repetitive but time-consuming operations like accounting and goods payment.
2. Transportation
Transport 3PL companies oversee moving goods or services between locations. One typical instance is when a 3PL company controls an inventory shipment between an organization and the buyer. Many 3PL providers for transportation frequently use other transportation companies to carry out the tasks for their partners.
3. Warehousing
One of the most popular kinds of third-party logistics providers is warehousing. An integrated warehouse 3PL that specializes in the storage and delivery of goods and/or services is part of a company’s warehousing and transportation operations. Several 3PL warehouse suppliers give flexible options for handling product transportation, distribution, and storage.
4. Distribution
A lot of 3PL companies also offer a wide range of wholesale and distribution services, such as manufacturing, picking, packing, and outbound order fulfillment. A small corporation may find it difficult to handle the effective distribution of big product volumes; by outsourcing distribution to a third-party logistics provider, employees can concentrate on other business duties that fall within their areas of expertise.
Advantages of 3PL Service Provider
There are various reasons why businesses use a 3PL for their logistical needs. Outsourcing to a third-party logistics provider can have several benefits, including time and cost savings as well as better and more affordable client experiences. Here are a few of the most widespread explanations why companies pick to work with a 3PL.
1. Scalability
Depending on the precise services required, a 3PL supplier can scale a business’s space, manpower, and transportation needs. Manufacturers, suppliers, and other manufacturers can expand into new markets more efficiently and in unique manners. A 3PL is made to streamline logistics tasks, which you might not be as familiar with, and open the door for more business expansion.
2. Time Saving & Cost Saving
A 3PL can have a significant impact in this situation because a corporation is aware that success depends on a specific level of efficiency. A 3PL eliminates those costs and frees up your key employees to concentrate on the manufacturing, strategic planning, and operational processes that better enable business growth as compared to allocating money and resources to building and maintaining a warehouse, figuring out how to transport goods and/or services, optimizing services, and keeping up with new technologies through an in-house management model.
3. Business Expansion
Using 3PL services, expanding a company into new markets and geographical locations, such as emerging nations, is now easier than ever. A business can access new markets, use new supply chains, and enhance customer service by collaborating with a 3PL. Such expansion is now more feasible than ever thanks to the availability of distribution centers and warehouses from third-party logistics companies, who frequently incorporate the required security and compliance measures into their service offerings and have attained the necessary accreditation to deliver worldwide services.
Disadvantages of 3PL
Using third-party logistics providers can have risks of its own despite the possible benefits. Here are a few of them:
1. Loss of Control
An organization gives up some control over the delivery when they choose a 3PL provider. When a company decides to work with a third-party logistics provider (3PL), they are placing a great deal of faith in the 3PL to uphold the agreed-upon SLAs, which are necessary for operations that may have a direct impact on customer satisfaction. If one of the parties is using inferior B2B integration software, the seamless interchange of crucial EDI and non-EDI information may be in danger.
2. Cost
Even while a 3PL can save a company a significant amount of time and money, external circumstances (tariffs, excessive regulation, weather, etc.) might result in rising expenses. A first financial analysis of a 3PL company may be beneficial, but you are then at the disposal of this external trading partner and its own corporate objectives.
3. Business Understanding
A standard 3PL might not be appropriate for your company if you operate in a highly regulated sector or have very specialized requirements (such as cold storage and temperature-controlled delivery). Furthermore, 3PLs frequently have hundreds or even thousands of customers, so they might not provide you with the individual attention you want. How accessible are they for support? How quickly can they fulfill your requests? It’s crucial to pick a 3PL that truly comprehends your company, its objectives, and how effective logistics and distribution can support those objectives.